What is MiCA?
The Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) introduces uniform EU-wide rules for crypto assets market. MiCA covers crypto assets that are not currently regulated by existing financial services legislation such as Directive 2014/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council (MiFID). Key provisions for those issuing and trading crypto assets (including asset-reference tokens and e-money tokens) cover disclosure requirements (e.g. whitepapers), authorization, market abuse prevention, consumer protection and supervision of transactions.
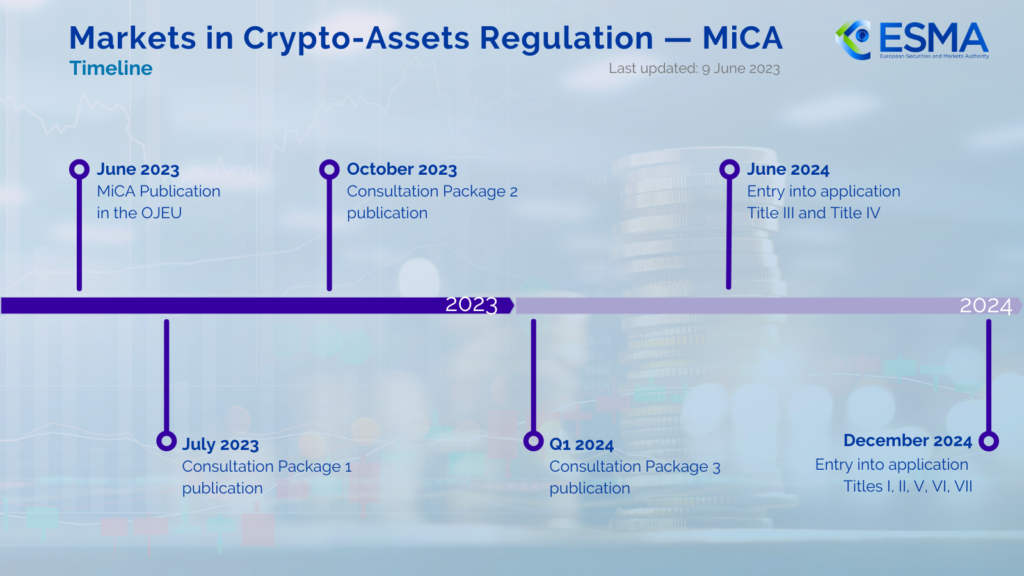
Below you can find a summary of key aspects that now effective MiCA will bring to the EU crypto market.
Scope
Some crypto assets are qualified as financial instruments and fall under the regime of MiFID. Other crypto assets, however, fall outside of the scope of Union legislative acts on financial services. MiCA aims to put in place specific rules for all, or a subset of, crypto assets that fall outside the scope of EU legislative acts on financial services, including cryptocurrencies, utility tokens, and stablecoins.
MiCA defines crypto assets as a digital representation of a value or of a right that is able to be transferred and stored electronically using distributed ledger technology (DLT) or similar technology.
Issuer Requirements
The issuance of crypto assets to the public will be subject to certain authorizations and requirements.
This includes requirements for marketing communication and obligation to draw up a crypto asset white paper. Issuers will have to publish their crypto-asset white papers and, where applicable, their marketing communications, on their website, which shall be publicly accessible.
Only entities that are legally authorized under MiCA or recognized as credit institutions will have the permission to issue asset-referenced tokens, while only credit institutions or those acting as electronic money institutions will be permitted to issue e-money tokens.
Authorization of CASP under MiCA
The regulation introduces a regulatory framework for crypto asset service providers, such as crypto exchanges and wallet providers. These entities will have to obtain authorization from national authorities to operate in the EU.
MiCA permits crypto asset service providers, who have operated in compliance with relevant legislation prior to December 30, 2024, to continue their activities until July 1, 2026, or until they receive or are denied MiCA authorization (a ‘grandfathering’ clause). However, in Lithuania a transitional period still under discussion. If transitional period is not applied, CASPs established in Lithuania will have to seek authorization by the end of 2024 to continue their operations.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) Rules
MICA integrates AML and CFT measures into the regulatory framework. Crypto asset service providers are expected to comply with AML and CFT regulations, including customer due diligence and reporting of suspicious transactions.
Market Abuse Provisions
The regulation includes provisions to prevent and address market abuse in the crypto asset markets. This involves measures to detect and deter manipulative practices and insider trading.
The rules on market abuse will apply to acts carried out by any person concerning crypto assets that are admitted to trading or in respect of which a request for admission to trading has been made.
Consumer Protection
MiCA emphasizes the importance of protecting consumers and investors in the crypto asset markets. This includes rules on the marketing of crypto assets and measures to ensure that consumers receive clear and comprehensible information.
Stablecoins
Specific rules are proposed for stablecoins, which are crypto assets designed to maintain a stable value. These rules include requirements for reserve assets, governance, and redemption mechanisms.
Supervision and Enforcement
National competent authorities are expected to supervise and enforce MiCA within their jurisdictions. In Lithuania, it is expected that the supervising authority will be the Bank of Lithuania.
Additionally, the timeline for the adoption and implementation of MICA could influence its actual impact on the crypto asset industry in Lithuania.
To learn more, you can view the full text of MiCA regulation or visit ESMA’s website.
